piRNA actively control transposable elements (TE) that would otherwise disrupt genes, chromosomal stability, damage DNA, cause inflammation, disease and/or cell death. For example, increased levels of endogenous retroviruses (ERV), a TE subclass, trigger fibro inflammation and play a role in kidney disease development. However, in mammals, the transcription of TEs is important for maintaining early embryonic development. piRNA also function with TE's for important aspects of Natural Killer (NK) cell immune development. Regardless of the cell type, endogenous retroviral elements of the ERV1 family, are highly enriched at p53 sites highlighting the importance of this repeat family in shaping the transcriptional network of p53.
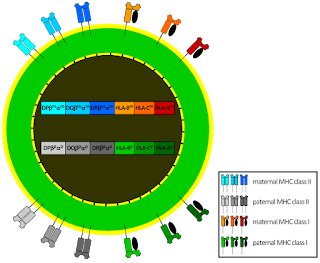
Decidual natural killer cells (dNK), the largest population of leukocytes at the maternal–fetal interface, have low cytotoxicity. They are believed to facilitate invasion of fetal HLA-G+ extravillous trophoblasts (EVT) into maternal tissues, essential for establishment of healthy pregnancies. dNK interaction with EVT leads to trogocytosis that acquires and internalizes HLA-G of EVT. dNK surface HLA-G was reacquired by incubation with EVT's. Activation of dNK by cytokines and/or viral products resulted in the disappearance of internalized HLA-G and restoration of cytotoxicity. Thus, the cycle provides both for NK tolerance and antiviral immune function by dNK.
A remote enhancer L, essential for HLA-G expression in EVT, describes the basis for its selective immune tolerance at the maternal–fetal interface. Found only in genomes that lack a functional HLA-G classical promoter it raises the possibility that a retroviral element was co-opted during evolution to function in trophoblast-specific tolerogenic HLA/MHC expression. CEBP and GATA regulate EVT expression of HLA-G through enhancer L isoforms.
HLA-G1 is acquired by NK cells from tumor cells, within minutes, by activated, but not resting NK cells via trogocytosis. Once acquired, NK cells stop proliferating, are no longer cytotoxic and behave as suppressors of cytotoxic functions in nearby NK cells via the NK ILT2 (Mir-7) receptor. Mir-7 is a well researched intervention target in inflammatory diseases and belongs to a p53-dependent non-coding RNA network and MYC signaling circuit.
Cells that transcribe enhancer L isoforms and HLA-G, feed NK cells with HLA-G as an innate element for self determination, similar to the way EVT's restrain cytotoxicity of dNK. Then incoming, NK cells at the periphery of tumor microenvironments (TME) may promote vascular remodeling, as in the uterus during pregnancy, by acidifying the extracellular matrix with a2V that releases bound pro-angiogenic growth factors trapped in the extracellular matrix. After that these incoming NK cells succumb to the influence of Mir-7 resulting in low cytotoxic, inactive NK in the TME.
Discovering resistant NK cells in the TME of a patient, for incubation, expansion and activation is a Codondex precision therapy objective based on p53 computations.